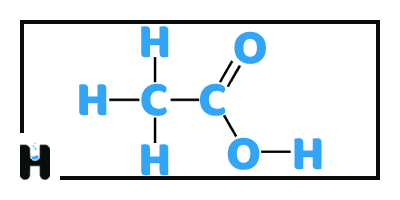
Acids
Acid is a molecule or an ion which is able to donating a proton (hydrogen ion , H⁺ ) this is definition knows as a Bronsted–Lowry acid. In some of aqueous solutions, a proton can donors form the hydronium ion H₃O⁺ and are known as Arrhenius acids. Bronsted and Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. The aqueous acidic solution has less than 7 pH, and as the acidity increase the value of pH will decrease.
The second definition is Lewis acids which can chemically accept pairs of electron from an atom in a base either directly or by losing hydrogen ion and this is considered as a generalization of the Bronsted definition.
Some Examples
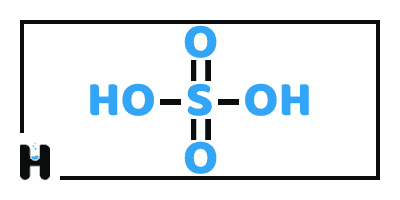
Sulfuric Acid
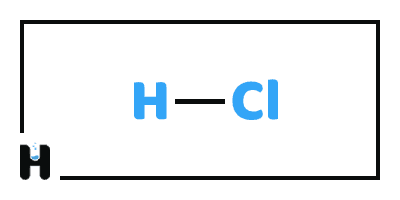
Hydrochloric Acid